- v1.0.0-latest-prod
The following data shows the key tables and persisted JSON structures used by the Auth Service.
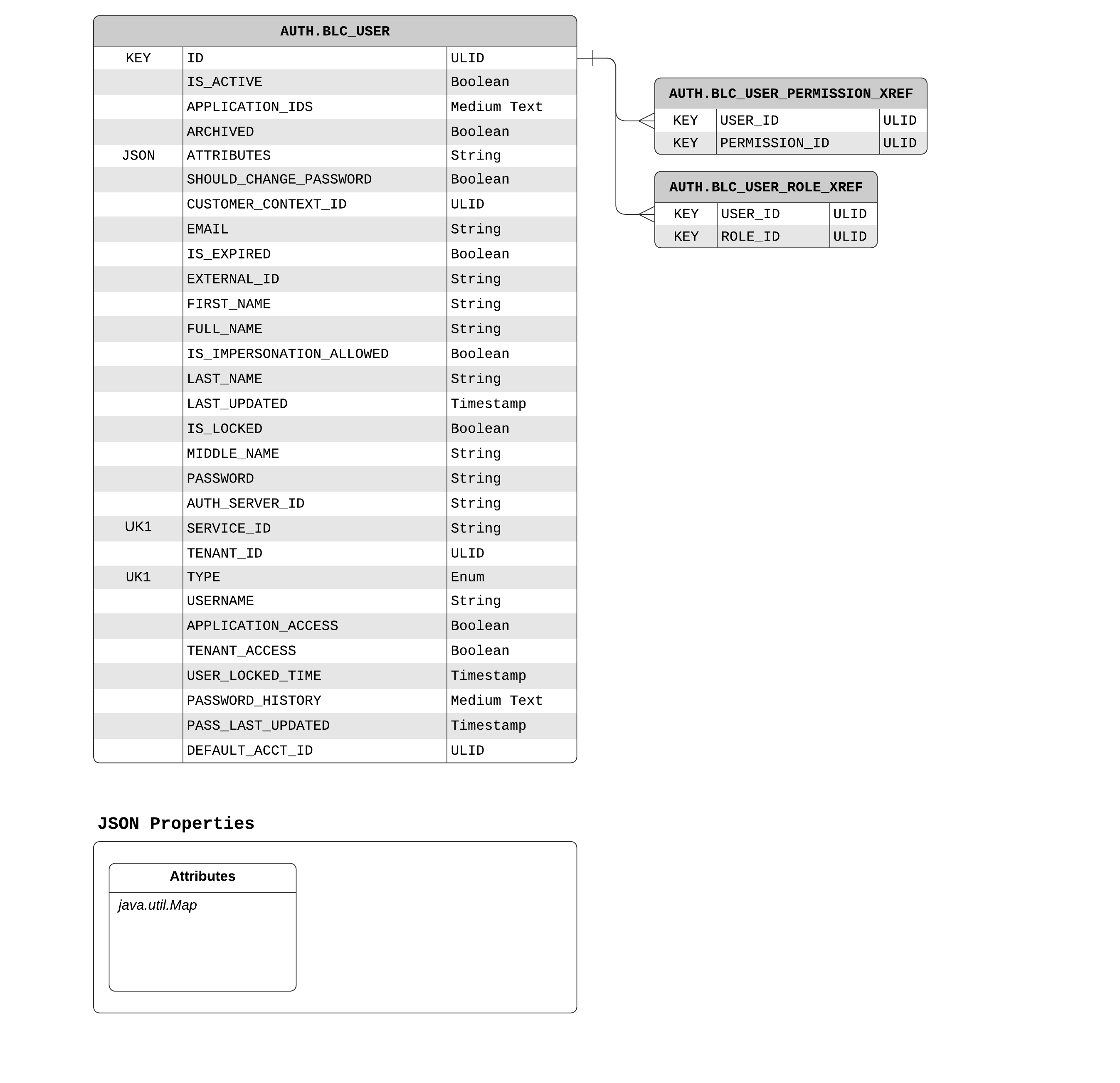
Represents a user which can authenticate with this service. Users can have UserRoles and UserPermissions. This domain is synchronized from other services such as the admin user service (AdminUserPersistenceHandler) and the customer service (CustomerPersistenceHandler).

Indicates which permissions have been granted to Users.
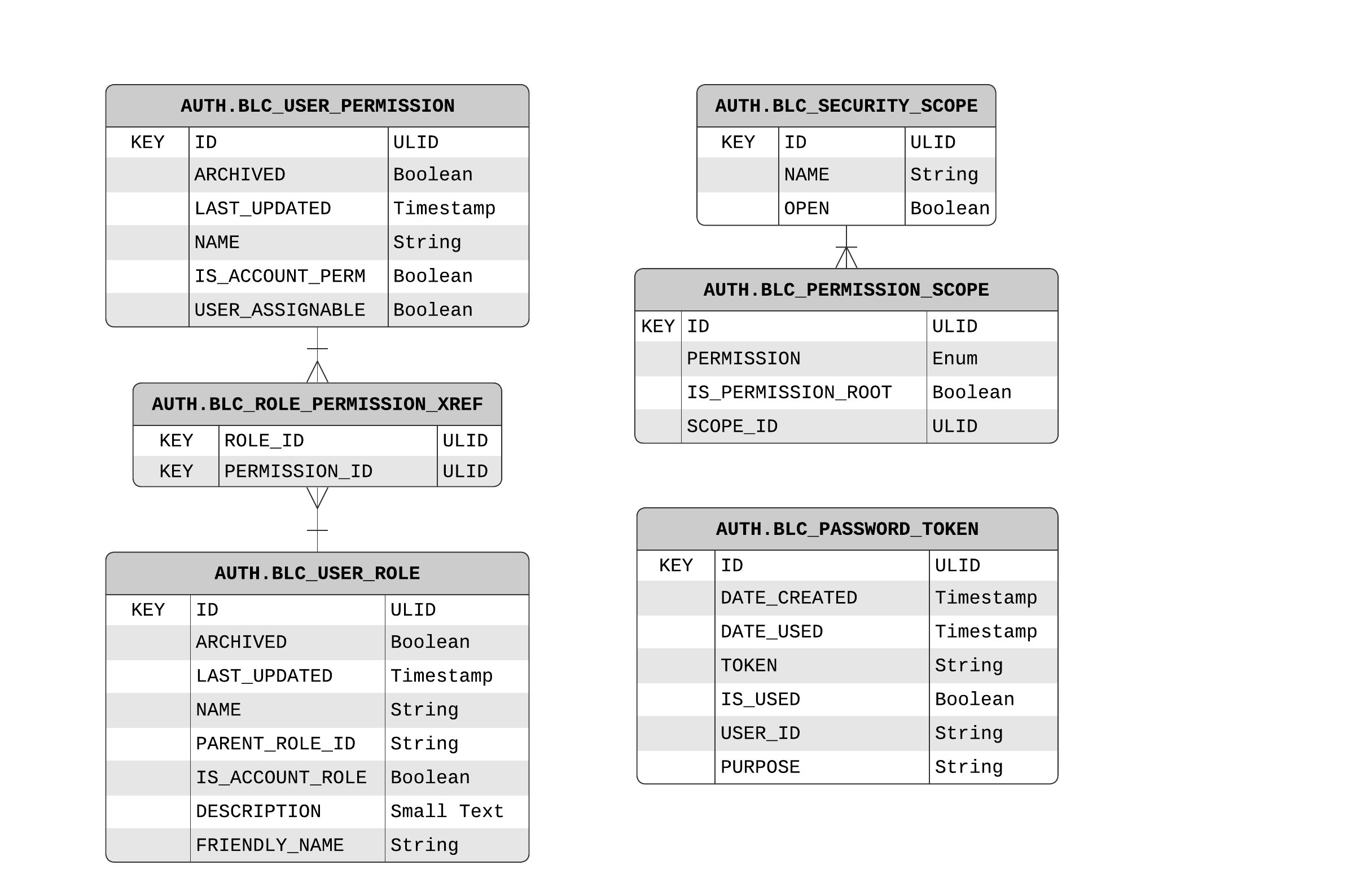
A string representation of a security role. A role represents a group of Permissions. Generally, a user is assigned a role like "Content Editor". The role would be setup to contain the permissions necessary to fulfill that role.
This domain also supports a hierarchical relationship with other roles. If a Role has a relation to a parent, then the role will effectively inherit all of the Permissions of its parent and any ancestors further up in the hierarchy
Roles can be associated with:
User
Authorization Server
A string representation of a security permission. A permission represents a privilige to do some functionality within the system. Examples would include things like ALL_PRODUCT, READ_PRODUCT, ALL_PRICE_LIST, READ_PRICE_LIST, etc…
Permissions can be associated with:
User
Authorization Server
Security Scope (indirectly)
A SecurityScope represents a set of permissions an application might want authorization for. This differs from a Role as a Security Scope primarily deals with facilitating the OAuth2 Authorization flow (whereas a Role primarily identifies a set of permissions assigned to a User).
For example, an application may want to request access to one or more scopes. In Broadleaf, a scope might be PRODUCT and contain the READ_PRODUCT, CREATE_PRODUCT, UPDATE_PRODUCT, and DELETE_PRODUCT permissions.
|
Note
|
When defining a |
Security Scopes can be associated with:
Authorized Clients (indirectly)
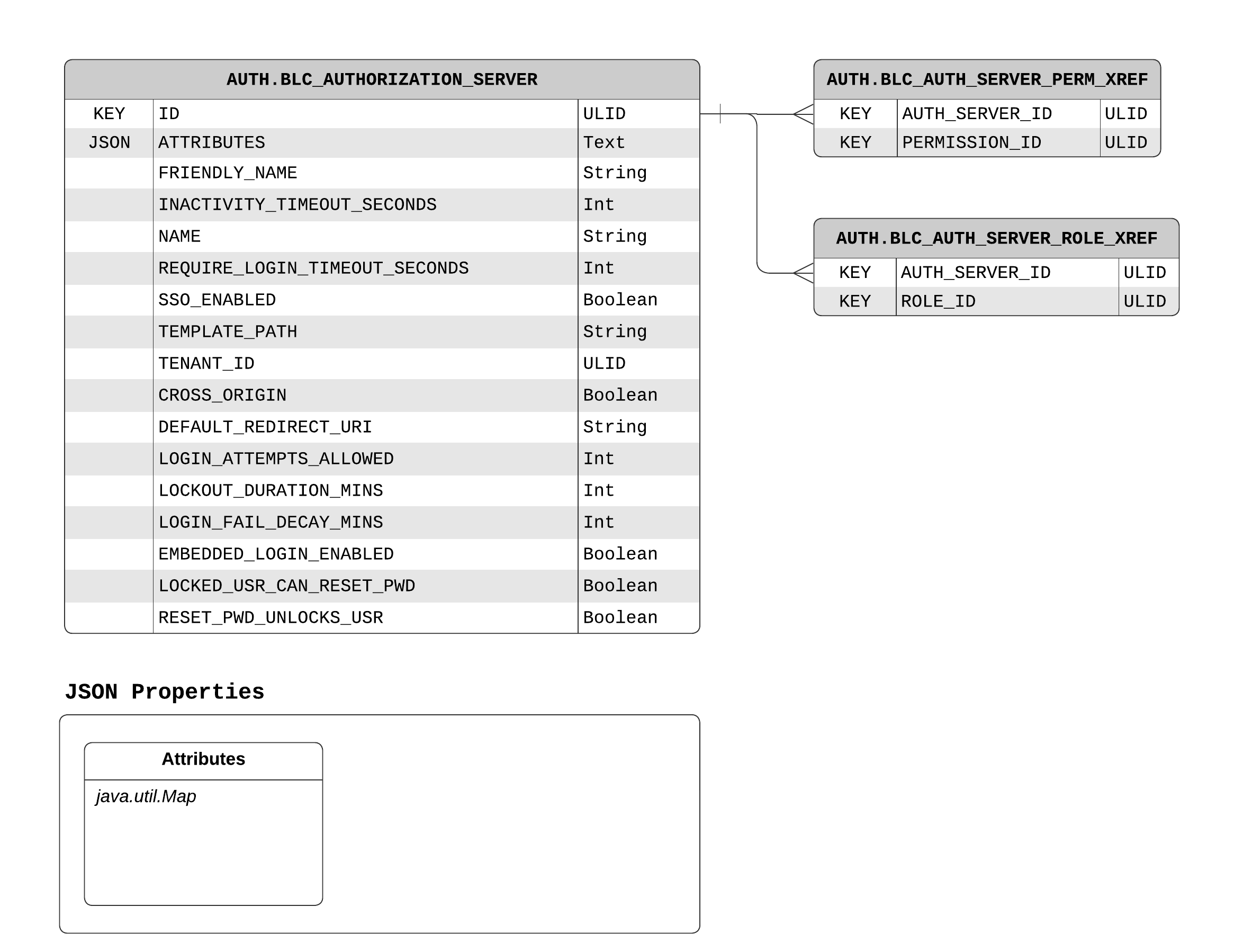
An authorization server is responsible for authenticating users. Generally, there are at least two authorization servers per tenant: one for customer users and one for admin users.
Users belong to an authorization server and are authenticated against it.
In the majority of cases, there is a 1-1 relationship between an AuthorizationServer and AuthorizedClient, though this is not a requirement.
In the case that an authorization server has multiple AuthorizedClients, users are shared between clients. This allows, for example, a tenant with multiple store-fronts to share a single login across different storefronts.
Keep in mind that any unique user requirements, such as unique email addresses, usernames, etc. are unique to an authorization server.
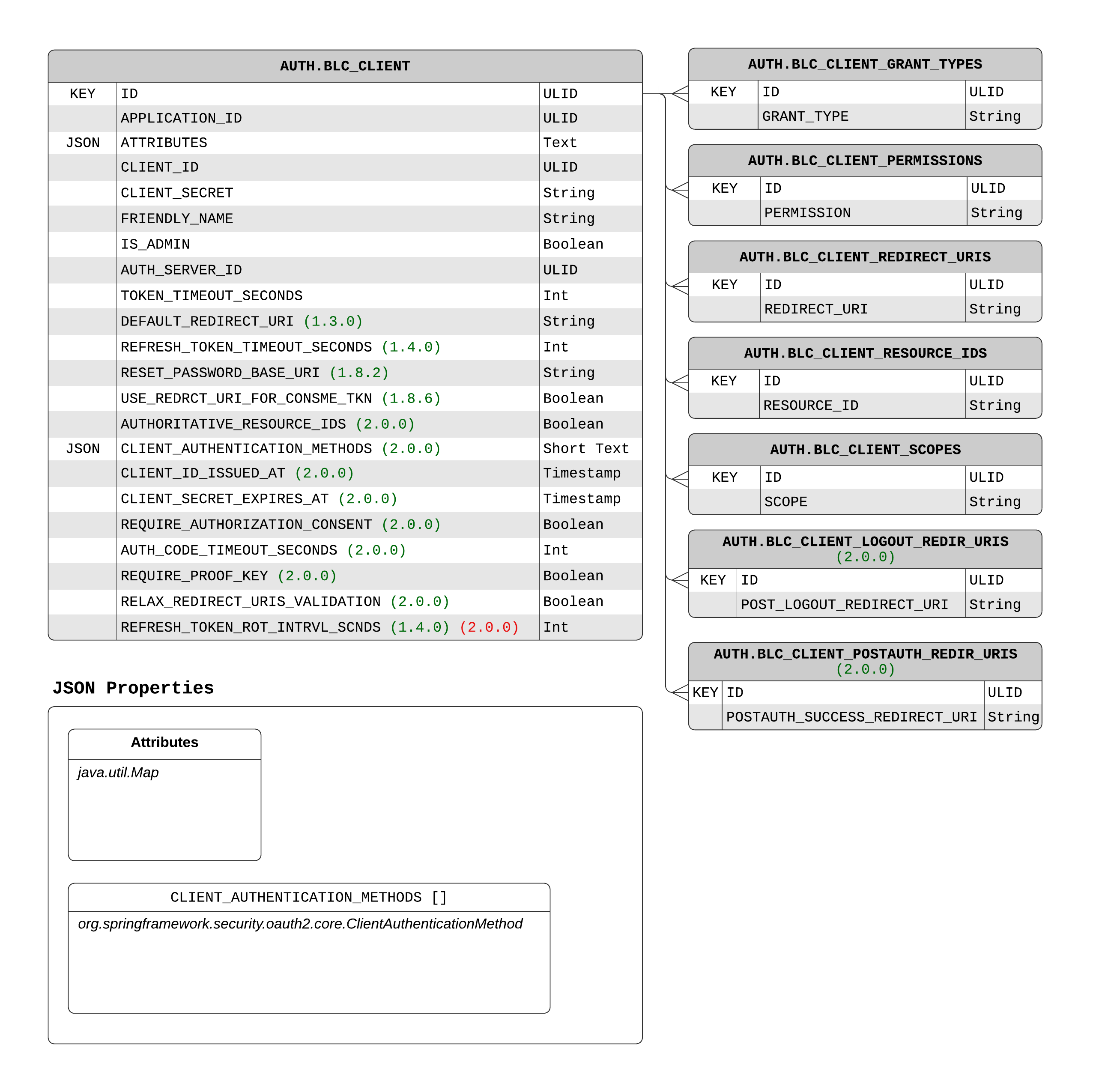
Represents the authorization service concept of an authorized client. This structure is used to store a persistent representation of a Spring Security OAuth2’s RegisteredClient for an AuthorizationServer.
Since AuthenticationServices 2.0, there are multiple types "redirect URI" fields available.
OAuth2 Redirect URIs - AuthorizedClient.redirectUris
Post-Authentication Success Redirect URIs (new in 2.0) - AuthorizedClient.postAuthenticationSuccessRedirectUris
Post-Logout Redirect URIs (new in 2.0) - AuthorizedClient.postLogoutRedirectUris
Default Redirect URI - AuthorizedClient.defaultRedirectUri
Previously, in AuthenticationServices 1.x, all redirect URIs were included in redirectUris. However, updates in the OAuth2 specification and Spring Security 6 require strict validation of OAuth2 redirect URIs. Since our other redirect URIs do not require strict validation, they have been moved to the fields postAuthenticationSuccessRedirectUris and postLogoutRedirectUris.
The postAuthenticationSuccessRedirectUris and postLogoutRedirectUris are whitelist fields. Authentication success and logout requests can include the returnTo parameter to indicate where the User should be forwarded after the operation. This parameter is compared against the appropriate redirect URI field to ensure a malicious actor is not forwarding the User to an unknown destination.
See Redirect URI Migration Notes for more information about migrating redirect URI fields during an upgrade from 1.x to 2.0.
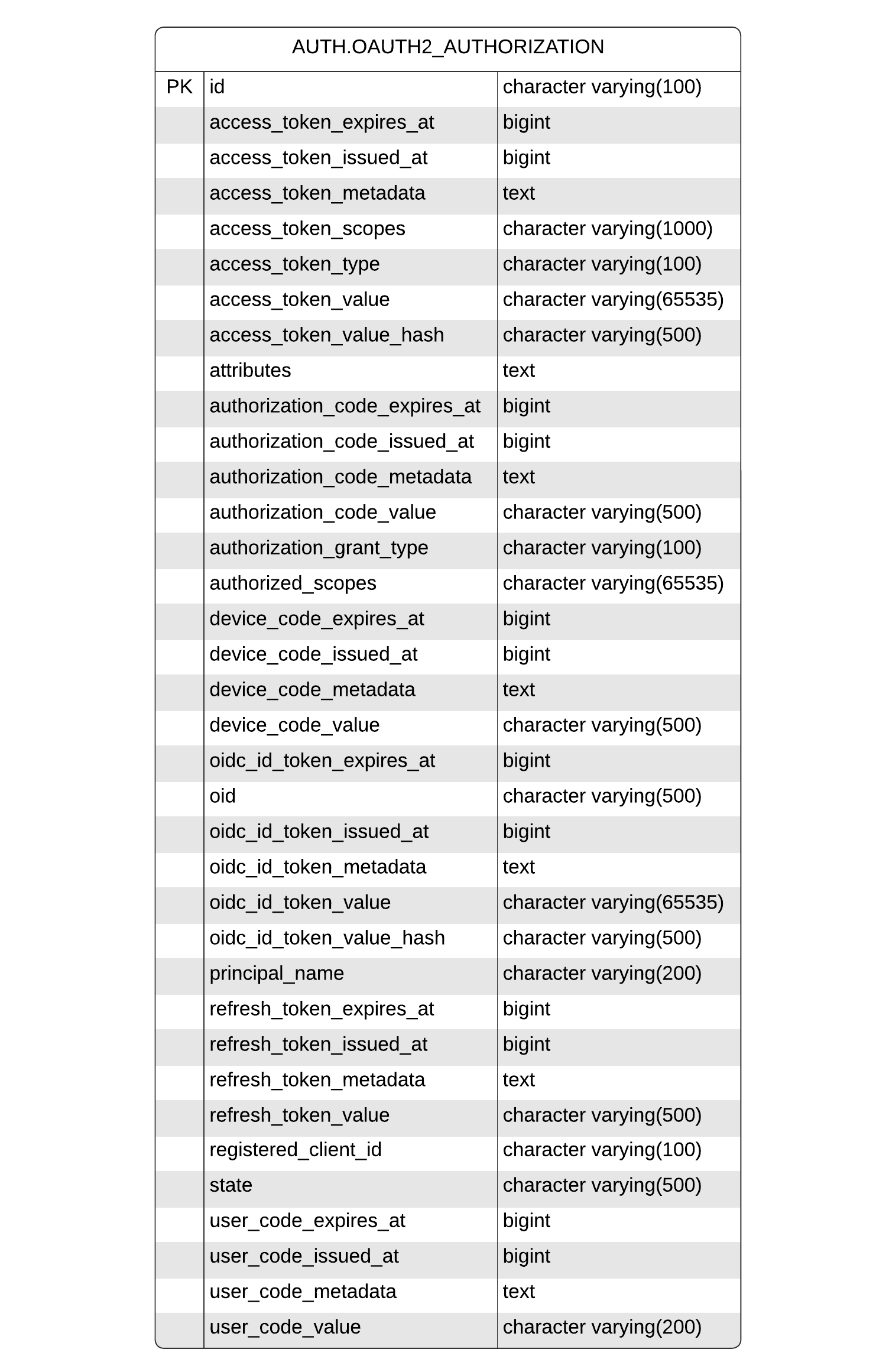
Spring Authorization Server uses the org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.authorization.OAuth2Authorization object to encapsulate data related to a user’s authorization, such as client name, principal name, authorized scopes, and access token. Spring Authorization Server includes the org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.authorization.OAuth2AuthorizationService to facilitate saving & loading OAuth2Authorization objects.
Broadleaf provides the DefaultOAuth2AuthorizationService and JpaOAuth2Authorization to facilitate saving & loading OAuth2Authorization objects with the database.