- v1.0.0-latest-prod
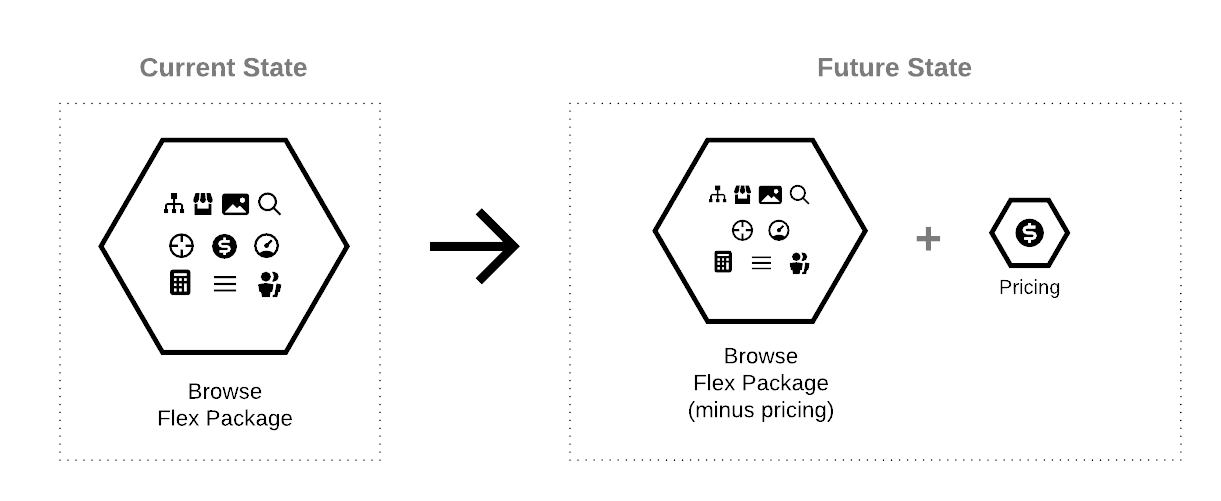
In this guide, we will go over the steps you will want to consider when moving from one Flex Package Composition to another. For example, we recommend that most Enterprise installations start with the Balanced Flex Package composition as defined here: Deployment Flexibility. Let’s say that after some time, you find that it would be beneficial to scale out a piece of it independently as it needs to have its own lifecycle. This is the scenario that we will be describing in this tutorial, as illustrated by the diagram below:

Many that are new to Broadleaf assume that moving from one Flex Package composition to another as being a "migration project" that might require significant application re-factoring or data migration. However, as long as you follow recommended microservice design and extension patterns, we believe that moving from one Flex Package to another is really an exercise of maintaining different deployment configurations.
That is - you can still be working with the same codebase, but will just need to maintain separate build configurations and properties to support deploying a different flex package composition
Given that Broadleaf is a microservices framework that can be extended with your own customizations, one big assumption that should be followed when doing so is making sure that any extensions or customizations do not cross bounded contexts.
Bounded Contexts in Broadleaf’s Microservice ecosystem are represented as the Resource Tier Services such as Catalog, Pricing, Customer, Offer, etc… where each utilizes its own data store for persistence.
Here’s as an example of an anti-pattern to watch out for: If you have an application that includes both the catalog and offer dependencies in the same deployable application, you should not create any hard dependencies between the two services. This would include directly calling each of these services APIs or creating new domains that cross boundaries (e.g. a Product-Offer Cross Reference that ties a product and offer together). Instead, you should use a messaging channel or leverage one of the Composite Tier Services to orchestrate communication across contexts (even if they are in the same deployable application).
Following these guidelines allows you to more easily move from one Flex Package composition to another.
The following section is only applicable to Initializr-based projects only (Release Train 1.8.4+)
With an initializr-based project, we’ve made it simple to change flex package compositions. All you would need to do is modify your manifest.yml file to create your own flex package component. Taking our example of splitting out Pricing from the Balanced - Browse Flex Package. You’ll notice that in your manifest.yml the following definition:
flexPackages:
- name: browse
domain:
cloud: browse
docker: browse
local: localhost
enabled: true
flexUnits: asset,catalog,catalogbrowse,content,menu,offer,pricing,ratings,vendor
messageInterlink:
suppressed: true
tenantSync: true
ports:
- debug: true
port: 9004
targetPort: 9004
- port: 9447
targetPort: 9447
The key property that needs modification is the flexUnits property (which defines which library components should be included) and currently contains the pricing library component.
Given that we want to extract pricing into its own flex component, all we would need to do is modify our manifest.yml with a similar configuration as below:
flexPackages:
- name: pricing
domain:
cloud: pricing
docker: pricing
local: localhost
enabled: true
flexUnits: pricing
ports:
- port: 8448
targetPort: 8448
- debug: true
port: 8005
targetPort: 8005
- name: browse
domain:
cloud: browse
docker: browse
local: localhost
enabled: true
flexUnits: asset,catalog,catalogbrowse,content,menu,offer,ratings,vendor
messageInterlink:
suppressed: true
tenantSync: true
ports:
- debug: true
port: 9004
targetPort: 9004
- port: 9447
targetPort: 9447
Once we have this defined, we can just run a ./mvnw clean install flex:generate in the manifest directory to re-build the project structure to match this configuration.
The following section is only applicable to legacy MicroservicesDemo-based projects only
Taking our example of splitting out Pricing from the Balanced - Browse Flex Package, the first thing you will want to do is remove your Pricing dependency from the Browse pom.xml.
|
Note
|
If you are working with our MicroservicesDemo starter project, you will see a library dependency called demo-pricing-services in flexpackages/balanced/browse/pom.xml which can be removed.
|
Removing this, will allow us to build a Spring Boot application that does not include the pricing dependency.
Next, you’re going to want to look at your Spring application context configurations.
Notice that in the Balanced - application-default.yml configuration, there are properties to configure Broadleaf’s Pricing service. You can spot it, as Broadleaf employs a Service Prefix properties convention to easily spot which configurations apply to which service.
For example:
broadleaf:
pricing:
liquibase:
change-log: 'classpath:/db/changelog/pricing.flexdemo.postgresql.changelog-master.yaml'
liquibase-schema: public
default-schema: pricing
delegating:
schema: pricing
delegate-ref: compositeSince we are removing the pricing depedency, we can also remove any configuration that enables it.
Since we are moving a service out of the Balanced - Browse Flex Package certain compositional services may be still configured to point to it as if it were still inside the Balanced - Browse package. For example: Cart Operations can be configured to set up the endpoints of where and how to call the Pricing Service like:
broadleaf:
catalogbrowse:
pricingprovider:
url: 'https://localhost:9447'Since we are no longer serving the Pricing Services API endpoints under the Browse deployment which by default listens on port 9447, we’ll want to change this to point to the correct URL that the new Pricing service is going to be listening on.
|
Tip
|
If using the MicroservicesDemo Starter Project, the Granular pricing service is set up to listen on port 8448
|
In our example, we want to deploy a granular Pricing Service. Luckily, the way our MicroservicesDemo starter project is set up, there is already configuration set up to deploy Pricing services indivdually using the localdev Spring Profile.
You will notice that under the maven structure in the project: services/pricing contains a fully executable Spring Boot application that can be run by itself (or built into a jar that is included in the Balanced - Browse application).
|
Tip
|
you can run Pricing by itself by going here cd /services/pricing and doing something like: ../../mvnw spring-boot:run -Dspring-boot.run.profiles=localdev
|
Finally, Broadleaf’s Reference Architecture employs a Gateway in front of these backend services to route requests from a client to the appropriate place. Since we’re splitting Pricing service outside of the Balanced - Browse Flex Package, we need to make sure that the request goes to the right place as illustrated in the diagram below:
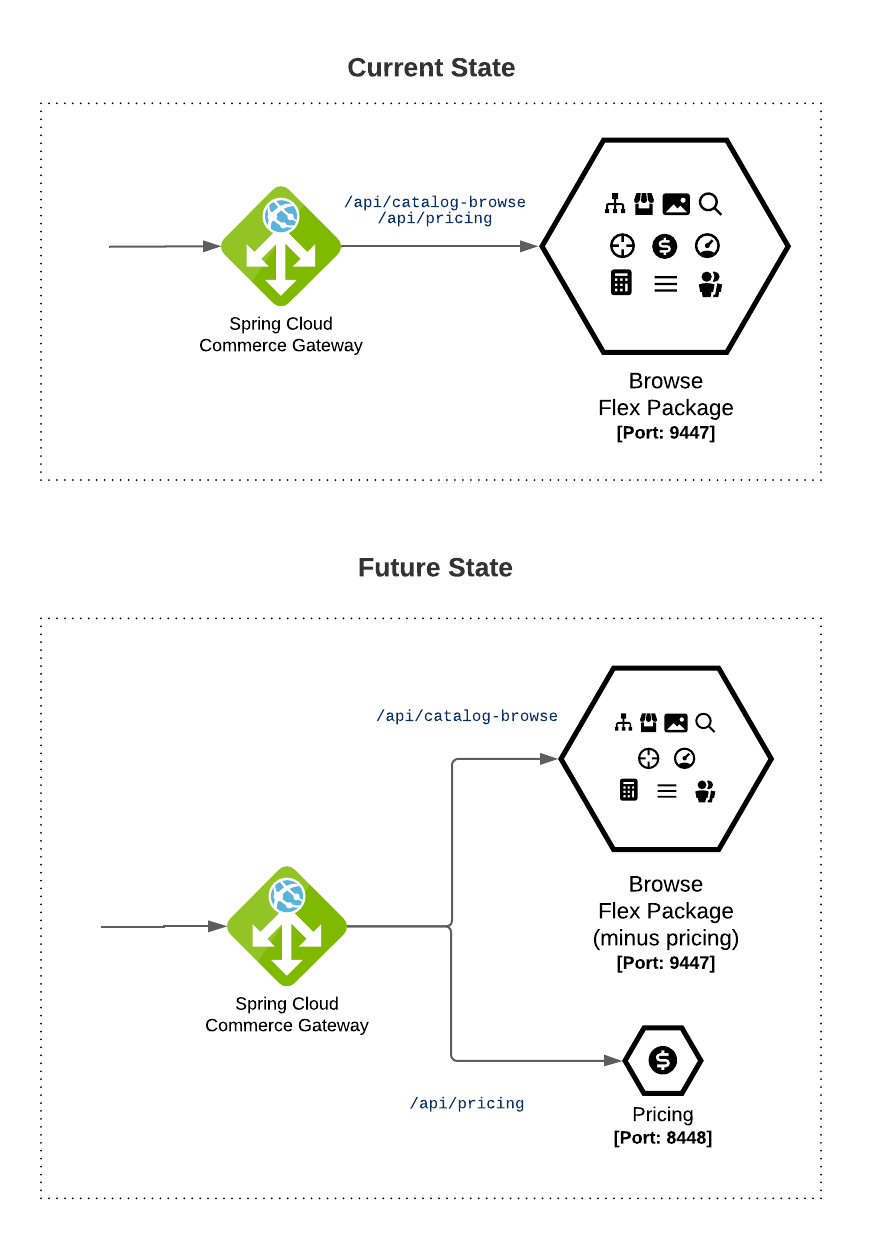
Since Spring Cloud Gateway routes are all configurable via Spring Application properties, this can all be changed using ENV runtime properties meaning that you don’t necessarily have to rebuild your application with new context files just to change an existing route.
For example, running this configuration locally using docker-compose, all you need to do is change the flexpackages/balanced/docker/.env file
from:
BROADLEAF_GATEWAY_PROXYURLS_PRICING=https://host.docker.internal:9447to
BROADLEAF_GATEWAY_PROXYURLS_PRICING=https://host.docker.internal:8448|
Tip
|
When deploying to kubernetes, you can pass in the same ENV overrides to the default helm charts as well. |